Overview
Cirrhosis of the liver is a progressive and irreversible condition characterized by the gradual replacement of healthy liver tissue with scar tissue, leading to impaired liver function. This scarring results from chronic liver damage caused by various factors such as alcohol abuse, viral hepatitis infections (such as hepatitis C and hepatitis B), metabolic disorders, autoimmune diseases, genetic conditions, and exposure to toxins.
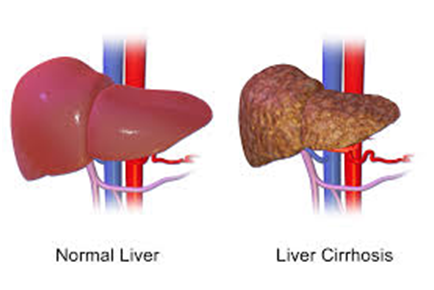
Stages of Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis progresses through stages, starting with compensated cirrhosis, where the liver can still function adequately despite the presence of scarring. However, as the disease advances, it enters the decompensated stage, where symptoms become more pronounced and liver function significantly declines.
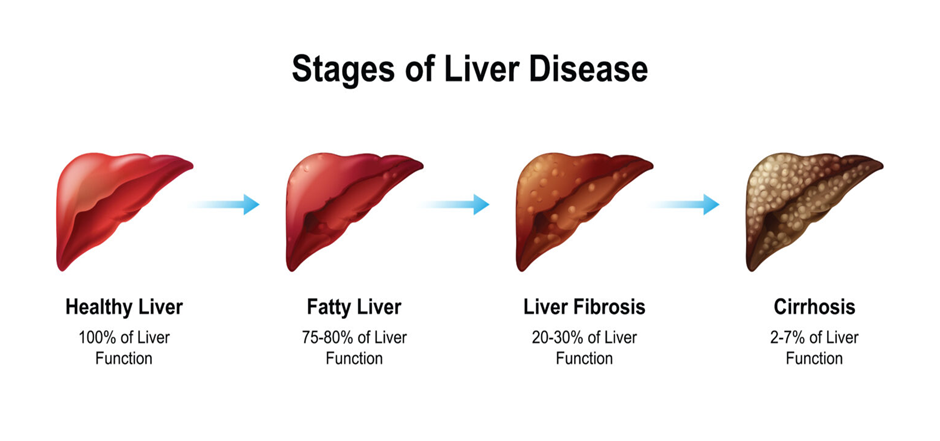
Effects of Cirrhosis
The scarring in the liver hinders its ability to perform essential functions, including filtering toxins from the blood, metabolizing nutrients, and producing vital proteins and enzymes. This can lead to various symptoms and complications, such as jaundice, ascites (fluid buildup in the abdomen), hepatic encephalopathy (brain dysfunction due to liver failure), and increased susceptibility to infections.
Prevalence and Symptoms
Cirrhosis is a prevalent condition globally, affecting millions of individuals, especially those in middle to late adulthood. Symptoms may vary depending on the stage of the disease, ranging from fatigue, nausea, and loss of appetite in the early stages to more severe manifestations like abdominal pain, swelling, and cognitive impairment as the disease progresses.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing cirrhosis, including excessive alcohol consumption, chronic viral hepatitis infections, obesity, diabetes, and certain genetic predispositions. Individuals with a history of heavy alcohol use, chronic hepatitis infections, or metabolic syndrome are particularly vulnerable to developing cirrhosis.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing cirrhosis typically involves a combination of physical examinations, blood tests to assess liver function, imaging studies (such as ultrasound or MRI), and sometimes a liver biopsy to confirm the presence of scarring. Treatment aims to manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and address underlying causes. This may involve lifestyle modifications, medications to manage complications, and, in severe cases, liver transplantation.
Prevention and Prognosis
Preventing cirrhosis involves adopting a healthy lifestyle, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, practicing safe sex to prevent hepatitis infections, maintaining a balanced diet, and managing underlying health conditions effectively. Prognosis varies depending on the stage of cirrhosis, the presence of complications, and the individual’s response to treatment. Regular monitoring by a qualified healthcare provider, such as the best physicians or MD medicine specialists in Gorakhpur, can help optimize management and improve outcomes.
FAQs
1. What are the early signs of cirrhosis?
– Early symptoms may include fatigue, nausea, loss of appetite, and upper abdominal pain.
2. Can cirrhosis be reversed?
– Cirrhosis involves permanent scarring of the liver, but progression can be slowed or halted with appropriate treatment.
3. How is cirrhosis diagnosed?
– Diagnosis typically involves a combination of physical exams, blood tests, imaging studies, and sometimes a liver biopsy.
4. What are the treatment options for cirrhosis?
– Treatment focuses on managing symptoms, addressing underlying causes, and preventing complications. This may include lifestyle changes, medications, and liver transplantation.
5. How can I prevent cirrhosis?
– Prevention involves adopting a healthy lifestyle, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, practicing safe sex, maintaining a balanced diet, and managing underlying health conditions effectively.
Individuals seeking specialized care for liver cirrhosis in Gorakhpur can consult Dr. Deepak Chandra Srivastava, the best physician in Gorakhpur with vast experience in managing patients.
